SEECIX route server guide
Route server information
SEECIX operates so-called route server systems (see RFC7947 for a detailed description) to facilitate the exchange of BGP announcements between peers at SEECIX. Each peer needs only to set up a BGP connection to the route server in order to receive the BGP announcements of all other peers having a BGP connection with the route server.
BGP session parameters
This section provides a brief overview of the BGP session parameters to connect to the route servers:
| rs1 | 185.1.172.252 2001:7f8:f5::de1a:a:1 |
| rs2 | 185.1.172.253 2001:7f8:f5::de1a:a:2 |
| AS | 56858 |
| Recommended prefix limit rs1/rs2 (your side) | IPv4: 250,000 IPv6: 70,000 |
BGP announcement filtering
This section describes the filtering mechanism that can be used to filter BGP announcements.
Your side
You can safely accept any BGP announcements received via all route servers as SEECIX filters all incoming BGP announcements from all peers. The filtering mechanism is described in the section "SEECIX side" below .
If you additionally want to filter on your side based on AS-SETs, you can do so by using one or more of the following AS-SETs registered in the RIPE database:
| RIR macro (AS-SET) | Purpose |
| AS-SEECIX | AS-SETs of all SEECIX customers (IPv4) |
| AS-SEECIX-V6 | AS-SETs of all SEECIX customers (IPv6) |
| AS-SEECIX-CONNECTED | ASNs of all SEECIX customers |
SEECIX side
At SEECIX, the route servers filter based on AS-path as well as IP prefixes. The BGP announcements that a route server receives from a peer are checked against the AS-SET the peer has provided. The AS-SET can be changed by contacting the SEECIX customer service team.
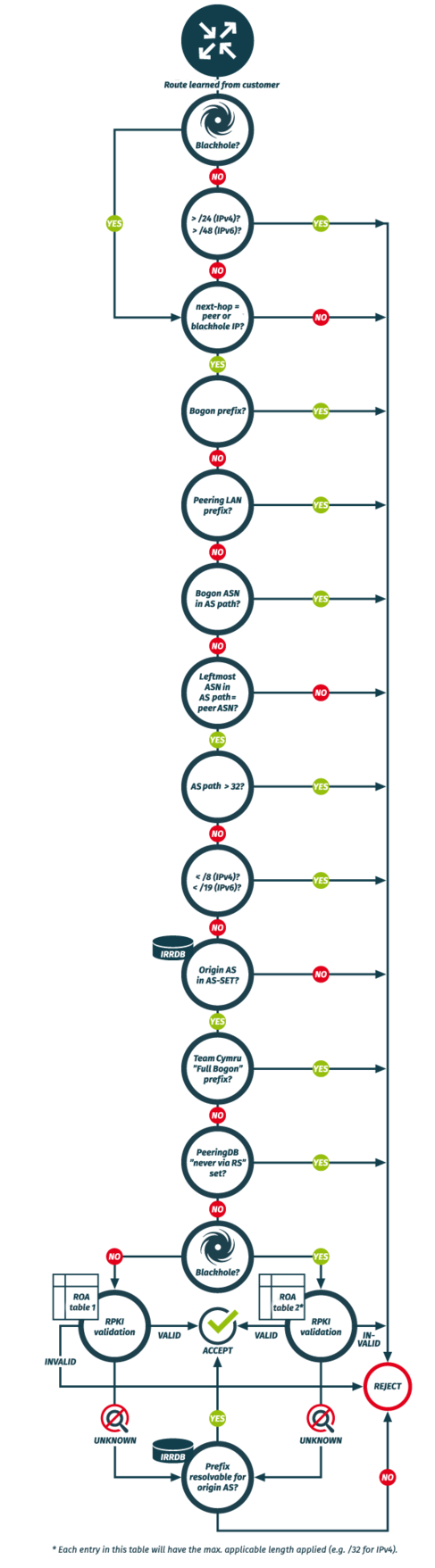
How and what the route servers filters
The SEECIX filters are updated every 6 hours. Do not forget to register your IP prefixes in the IRR database well in advance (at least 24h before announcing the first time).
Bogon and Martian filtering
Please make sure not to announce routes that
- are > /24 (IPv4) and > /48 (IPv6) (RFC7454)
- have a different BGP next-hop than the IP of your own router
- are bogons/martians (private and reserved IP prefixes as defined by RFC1918, RFC2544, RFC3927, RFC 5735, RFC5737, RFC6598 and RFC6890)
- are a SEECIX peering LAN (please also do not announce any of our peering LANs in the DFZ!)
- contain bogon ASNs in the BGP AS path (private and reserved ASN numbers as defined by RFC7607, RFC6793, RFC5398, RFC6996, RFC7300)
- differ in the leftmost ASN in the AS path from your own ASN
- have an AS path length > 32
- are < /8 (IPv4) and < /16 (IPv6) (RFC7454)
- are listed in the Team Cymru Fullbogon list
- are marked as "never via route servers" in PeeringDB
We will drop these kinds of routes.
Check the status of your routes
You can check the status of your announced routes to us in our Looking Glass. The reason why a route is filtered is also shown, as is a hint on how to fix the issue.
IRR and RPKI validation
Any routes you announce will also be RPKI (RFC6811, RFC7115) validated and checked against Internet Routing Registry (IRR) data. The AS-SET you provide to us will be recursively resolved. Then filtering is executed as follows:
- Origin ASN needs to be in customer cone (make sure that your AS-SET is well maintained and that all your downstreams are included)
- Is the route a blackhole (RFC7999)?
- If no, the route undergoes strict RPKI validation filtering (both origin and maxLength):
- if the result is RPKI Valid, the route is accepted (a missing route object will have no implication in this case)
- if the result is RPKI Invalid, the route is rejected
- if the result is RPKI NotFound/Unknown, we check if the route is resolvable for its origin ASN (this will be the case if a proper route object exists) and it might get accepted or rejected depending on the result**
- If yes, the route undergoes loose RPKI validation filtering (origin only):
- if the result is RPKI Valid, the route is accepted
- if the result is RPKI Invalid, the route is rejected
- if the result is RPKI NotFound/Unknown, we check if the route is resolvable for its origin ASN (this will be the case if a proper route object exists) and it might get accepted or rejected depending on the result**
- If no, the route undergoes strict RPKI validation filtering (both origin and maxLength):
**Loose filtering on IRRDB route objects
We perform loose filtering on IRRDB route objects. For example: If you have a route object for 46.31.120.0/21 we will also accept e.g. 46.31.120.0/22 and other more specifics (up to /24 and up to /32 for blackholes). If this is not a desired behavior, we strongly encourage you to create a ROA and set the maxLength attribute accordingly. As RPKI validation is performed before the IRRDB route object check, it will render all undesired more specifics as RPKI Invalid, which will result in rejection of these. Please note that this method only works for non-blackholes as we perform loose RPKI validation on blackholes (i.e. ignore maxLength).
Route server setup
The route server setup at SEECIX consists of two machines. The software utilized to provide the route server service is BIRD. Of the two route servers only one is required. However, in order to use the route server service, every peer is requested to connect to both machines for redundancy purposes, so that if one machine is out of order (e.g. maintenance), the route server service can still be used.
If the route servers system receive a BGP announcement marked as a Blackhole, the NO-EXPORT community and the BLACKHOLE Community are added if these communities are not already present. This makes sure each BGP announcement marked as Blackhole can be easily filtered and does not spread widely in the Internet routing system.
Route server control
Action BGP Communities can be used to control various functions of the route server. With this communities, you can:
- control the redistribution of advertised prefixes (on an ASN or geo location basis)
- prepend your own ASN up to three times
- trigger the calculation of a new alternate path (if available) for your advertised prefixes before you start commencing a maintenance
More information can be found here.
Route server prefix information
Informational BGP Communities are used to signal various information about redistributed prefixes. The SEECIX route servers tag all prefixes with certain BGP Communities to indicate their origin. You can use this information to determine where a certain prefix has been injected into the SEECIX switching platform. This gives you the possibility to filter routes learned from the route servers based on geographical location.
More information can be found here.
Route server session types
We offer two session types:
Standard/public session (default)
- We re-distribute all your announcements to other peers while honoring the BGP Communities which allow you to restrict your announcements
- We advertise all announcements from other peers to you while honoring the BGP Communities which allow others peers to restrict their announcements
Monitor session
From an operational point of view, it is advised to set up BGP sessions to both route servers, even if you do not want to peer with (i.e. advertise prefixes to) the route servers. This helps SEECIX staff to quickly monitor the availability of each peer.
Please note that you are required to set up BGP sessions with (but don not need to advertise prefixes to) the SEECIX route servers to be able to claim credits for the GlobePEER service. Otherwise SEECIX may not be able to comply with its SLA.
If your decision not to establish BGP sessions with the route servers was made due to your peering policy, please contact us for establishing a monitoring only session. You don’t have to advertise any prefixes and you won’t receive any prefixes from us on that session.
Example configurations
The following section contains configurations examples for different router operating systems:
! ! Config example for Cisco IOS ! Peer and session templates, (S)AFI format and some basic filtering ! DE-CIX route servers rs1, rs2 ! Your example ASN: 64500 (replace with your real ASN) ! Local preference route servers: 125 ! router bgp 64500 bgp router-id! Requires all your sessions to reset to take effect (if not already enabled) bgp graceful-restart bgp graceful-restart restart-time 120 bgp graceful-restart stalepath-time 360 template peer-policy PP_DECIX_ROUTE_SERVERS_COMMON ! Optional: Keep a pre-ingress-route-map copy of the peer table (if you have the memory; useful for debugging) soft-reconfiguration inbound ! Strip private ASNs from BGP AS-PATH remove-private-as ! Allow sending of BGP standard communities to control your prefix advertisements ! For all available communities, please see "Action BGP Communities" send-community exit-peer-policy ! template peer-policy PP_DECIX_ROUTE_SERVERS_4 ! Apply ingress route map route-map RM_DECIX_ROUTE_SERVERS_IN in ! Apply egress IPv4 route map route-map RM_DECIX_ROUTE_SERVERS_OUT_4 out ! Please set maximum-prefix limit IPv4 mentioned in the RS Guide/Peering DB ! maximum-prefix inherit peer-policy PP_DECIX_ROUTE_SERVERS_COMMON 1 exit-peer-policy ! template peer-policy PP_DECIX_ROUTE_SERVERS_6 ! Apply ingress route map route-map RM_DECIX_ROUTE_SERVERS_IN in ! Apply egress IPv6 route map route-map RM_DECIX_ROUTE_SERVERS_OUT_6 out ! Please set maximum-prefix limit IPv6 mentioned in the RSGuide/Peering DB ! maximum-prefix inherit peer-policy PP_DECIX_ROUTE_SERVERS_COMMON 1 exit-peer-policy ! template peer-session PS_DECIX_ROUTE_SERVERS ! ASN of DE-CIX route servers remote-as 56858 ! The route servers are passive and waiting for you side to initiate the sessions transport connection-mode active ! Use BGP version 4 and skip version negotiation version 4 ! Please do not use aggressive timers (60/180 should be fine) to reduce the risk of flapping sessions timers 60 180 exit-peer-session ! ! Our route servers are transparent: Ignore first AS in AS path not being your peer AS (i.e. 56858) no bgp enforce-first-as bgp log-neighbor-changes neighbor 185.1.172.252 inherit peer-session PS_DECIX_ROUTE_SERVERS neighbor 185.1.172.252 description RS1.SEECIX.NET neighbor 2001:7f8:f5::de1a:a:1 inherit peer-session PS_DECIX_ROUTE_SERVERS neighbor 2001:7f8:f5::de1a:a:1 description RS1.SEECIX.NET neighbor 185.1.172.253 inherit peer-session PS_DECIX_ROUTE_SERVERS neighbor 185.1.172.253 description RS2.SEECIX.NET neighbor 2001:7f8:f5::de1a:a:2 inherit peer-session PS_DECIX_ROUTE_SERVERS neighbor 2001:7f8:f5::de1a:a:2 description RS2.SEECIX.NET ! address-family ipv4 unicast ! Some example IPv4 prefixes to announce network 192.0.2.0 network 198.51.100.0 network 203.0.113.0 ! We do not support IPv6 over IPv4 transport no neighbor 2001:7f8:f5::de1a:a:1 activate no neighbor 2001:7f8:f5::de1a:a:2 activate neighbor 185.1.172.252 activate neighbor 185.1.172.252 inherit peer-policy PP_DECIX_ROUTE_SERVERS_4 neighbor 185.1.172.253 activate neighbor 185.1.172.253 inherit peer-policy PP_DECIX_ROUTE_SERVERS_4 exit-address-family ! address-family ipv6 unicast ! Some example IPv6 prefixes to announce network 2001:DB8:1234::/48 network 2001:DB8:ABCD::/48 network 2001:DB8:FFFF::/48 neighbor 2001:7f8:f5::de1a:a:1 activate neighbor 2001:7f8:f5::de1a:a:1 inherit peer-policy PP_DECIX_ROUTE_SERVERS_6 neighbor 2001:7f8:f5::de1a:a:2 activate neighbor 2001:7f8:f5::de1a:a:2 inherit peer-policy PP_DECIX_ROUTE_SERVERS_6 exit-address-family ! ! Use new BGP community format ip bgp-community new-format ! ! We will not advertise IPv4 prefixes less specific than /8 and more specific than /24 ! Exception: Blackhole next-hop and/or BLACKHOLE Community is set. ! Please allow up to /32 if you wish to receive all blackholed prefixes from the route servers ! Prefix list example: Allow every IPv4 prefix up to /32 from the route servers ip prefix-list PL_DECIX_ROUTE_SERVERS_IN_4 seq 5 permit 0.0.0.0/0 le 32 ! ! We will not advertise IPv6 prefixes less specific than /19 and more specific than /48 ! Exception: Blackhole next-hop and/or BLACKHOLE Community is set. ! Please allow up to /128 if you wish to receive all blackholed prefixes from the route servers ! Prefix list example: Allow every IPv6 prefix up to /128 from the route servers ipv6 prefix-list PL_DECIX_ROUTE_SERVERS_IN_6 seq 5 permit ::/0 le 128 ! ! We do not accept IPv4 prefixes less specific than /8 and more specific than /24 ! Exception: Up to /32 allowed when Blackhole next-hop and/or BLACKHOLE Community is set ! Prefix list example: Make sure to only advertise your own IPv4 prefixes/those of your customers ip prefix-list PL_DECIX_ROUTE_SERVERS_OUT_4 seq 5 permit 192.0.2.0/24 ip prefix-list PL_DECIX_ROUTE_SERVERS_OUT_4 seq 10 permit 203.0.113.0/24 ! ! We do not accept IPv6 prefixes less specific than /19 and more specific than /48 ! Exception: Up to /128 allowed when Blackhole next-hop and/or BLACKHOLE Community is set ! Prefix list example: Make sure to only advertise your own IPv6 prefixes/those of your customers ipv6 prefix-list PL_DECIX_ROUTE_SERVERS_OUT_6 seq 5 permit 2001:DB8:1234::/48 ipv6 prefix-list PL_DECIX_ROUTE_SERVERS_OUT_6 seq 10 permit 2001:DB8:FFFF::/48 ! ! Prefix list example: IPv4 prefixes to blackhole ip prefix-list PL_DECIX_BLACKHOLE_OUT_4 seq 5 permit 198.51.100.0/24 ! ! Prefix list example: IPv6 prefixes to blackhole ipv6 prefix-list PL_DECIX_BLACKHOLE_OUT_6 seq 5 permit 2001:DB8:ABCD::/48 ! ! Route-Map example: Set local-preference for route servers to 125 route-map RM_DECIX_ROUTE_SERVERS_IN permit 10 match ip address prefix-list PL_DECIX_ROUTE_SERVERS_IN_4 match ipv6 address prefix-list PL_DECIX_ROUTE_SERVERS_IN_6 set local-preference 125 ! ! Route-Map example: ! Use community 0:64501 for not allowing AS64501 to receive your prefixes ! Use community 56858:56858 for allowing the route servers to advertise your prefixes to all (other) peers ! For all available communities, please see "Action BGP Communities" route-map RM_DECIX_ROUTE_SERVERS_OUT_4 permit 10 match ip address prefix-list PL_DECIX_ROUTE_SERVERS_OUT_4 set community 56858:56858 0:64501 additive ! ! Route-Map example: Blackhole IPv4 prefixes route-map RM_DECIX_ROUTE_SERVERS_OUT_4 permit 20 match ip address prefix-list PL_DECIX_BLACKHOLE_OUT_4 set community 56858:56858 additive set community 65535:666 additive ! ! Route-Map example: ! Use community 0:56858 in combination with 56858:64502 to allow no one except AS64502 to receive your IPv6 prefixes route-map RM_DECIX_ROUTE_SERVERS_OUT_6 permit 10 match ipv6 address prefix-list PL_DECIX_ROUTE_SERVERS_OUT_6 set community 0:56858 additive set community 56858:64502 additive ! ! Route-Map example: Blackhole IPv6 prefixes route-map RM_DECIX_ROUTE_SERVERS_OUT_6 permit 20 match ipv6 address prefix-list PL_DECIX_BLACKHOLE_OUT_6 set community 56858:56858 additive set community 65535:666 additive !
!!
!! Config example for Cisco IOS XR
!! Session-, AF- and neighbor groups as well as some basic filtering
!! DE-CIX route servers rs1, rs2
!! Your example ASN: 64500 (replace with your real ASN)
!! Local preference route servers: 125
!!
!
!! We do not accept IPv4 prefixes less specific than /8 and more specific than /24
!! Exception: Up to /32 allowed when Blackhole next-hop and/or BLACKHOLE Community is set
!! Prefix set example: Make sure to only advertise your own IPv4 prefixes/those of your customers
prefix-set PS_DECIX_ROUTE_SERVERS_OUT_4
192.0.2.0/24,
203.0.113.0/24
end-set
!
!! We do not accept IPv6 prefixes less specific than /19 and more specific than /48
!! Exception: Up to /128 allowed when Blackhole next-hop and/or BLACKHOLE Community is set
!! Prefix set example: Make sure to only advertise your own IPv6 prefixes/those of your customers
prefix-set PS_DECIX_ROUTE_SERVERS_OUT_6
2001:db8:1234::/48,
2001:db8:ffff::/48
end-set
!
!! Prefix set example: IPv4 prefixes to blackhole
prefix-set PS_DECIX_BLACKHOLE_OUT_4
198.51.100.0/24
end-set
!
!! Prefix set example: IPv6 prefixes to blackhole
prefix-set PS_DECIX_BLACKHOLE_OUT_6
2001:db8:abcd::/48
end-set
!
!! Use this community for allowing the route servers to advertise your prefixes to all peers
!! For all available communities, please see "Action BGP Communities"
!! Community set example: Community set for DE-CIX "advertise to all peers" community
community-set CS_DECIX_ADVERTISE_TO_ALL_PEERS
56858:56858
end-set
!
community-set CS_DECIX_BLACKHOLE
65535:666
end-set
!
!! We will not advertise IPv4 prefixes less specific than /8 and more specific than /24
!! Exception: Blackhole next-hop and/or BLACKHOLE Community is set
!! Please allow up to /32 if you wish to receive all blackholed prefixes from the route servers
!! Route Policy example: Allow every IPv4 prefix from the route servers and set local preference to 125
route-policy RPL_DECIX_ROUTE_SERVERS_IN_4
set local-preference 125
pass
end-policy
!
!! We will not advertise IPv6 prefixes less specific than /19 and more specific than /48
!! Exception: Blackhole next-hop and/or BLACKHOLE Community is set
!! Please allow up to /128 if you wish to receive all blackholed prefixes from the route servers
!! Route Policy example: Allow every IPv6 prefix from the route servers and set local preference to 125
route-policy RPL_DECIX_ROUTE_SERVERS_IN_6
set local-preference 125
pass
end-policy
!
!! Route Policy example:
!! Advertise IPv4 prefixes from prefix sets PS_DECIX_ROUTE_SERVERS_OUT_4 and PS_DECIX_BLACKHOLE_OUT_4 (prefixes to blackhole)
!! Use community 0:64501 for not allowing AS64501 to receive your prefixes
!! Use community 56858:56858 for allowing the route servers to advertise your prefixes to all (other) peers
!! Set DE-CIX BLACKHOLE Community
!! For all available communities, please see "Action BGP Communities"
route-policy RPL_DECIX_ROUTE_SERVERS_OUT_4
if destination in PS_DECIX_ROUTE_SERVERS_OUT_4 then
set community CS_DECIX_ADVERTISE_TO_ALL_PEERS additive
set community (0:64501) additive
pass
!! Blackhole IPv4 prefixes
elseif destination in PS_DECIX_BLACKHOLE_OUT_4 then
!! Allow all peers to receive your blackholed prefixes
set community CS_DECIX_ADVERTISE_TO_ALL_PEERS additive
!! Set BLACKHOLE Community
set community CS_DECIX_BLACKHOLE additive
pass
else
drop
endif
end-policy
!
!! Route Policy example:
!! Advertise IPv6 prefixes from prefix sets PS_DECIX_ROUTE_SERVERS_OUT_6 and PS_DECIX_BLACKHOLE_OUT_6 (prefixes to blackhole)
!! Use community 0:56858 in combination with 56858:64502 to allow no one except AS64502 to receive your IPv6 prefixes
!! Set DE-CIX BLACKHOLE Community
route-policy RPL_DECIX_ROUTE_SERVERS_OUT_6
if destination in PS_DECIX_ROUTE_SERVERS_OUT_6 then
set community (0:56858) additive
set community (56858:64502) additive
pass
!! Blackhole IPv6 prefixes
elseif destination in PS_DECIX_BLACKHOLE_OUT_6 then
!! Allow all peers to receive your blackholed prefixes
set community CS_DECIX_ADVERTISE_TO_ALL_PEERS additive
!! Set BLACKHOLE Community
set community CS_DECIX_BLACKHOLE additive
pass
else
drop
endif
end-policy
!
router bgp 64500
bgp router-id
bgp graceful-restart
address-family ipv4 unicast
!! Some example IPv4 prefixes to announce
network 192.0.2.0/24
network 198.51.100.0/24
network 203.0.113.0/24
!
address-family ipv6 unicast
!! Some example IPv6 prefixes to announce
network 2001:db8:1234::/48
network 2001:db8:abcd::/48
network 2001:db8:ffff::/48
!
af-group AG_DECIX_ROUTE_SERVERS_4 address-family ipv4 unicast
!! Allow sending of BGP standard communities to control your prefix advertisements
!! For all available communities, please see "Action BGP Communities"
send-community-ebgp
!! Inbound IPv4 policy
route-policy RPL_DECIX_ROUTE_SERVERS_IN_4 in
!! Outbound IPv4 policy
route-policy RPL_DECIX_ROUTE_SERVERS_OUT_4 out
!! Please set maximum-prefix limit IPv4 mentioned in the RS Guide/Peering DB
!! maximum-prefix 75
!! Strip private ASNs from BGP AS-PATH
remove-private-AS
!! Optional: Keep a pre-ingress-route-map copy of the peer table even if route refresh is supported (if you have the memory; useful for debugging)
soft-reconfiguration inbound always
!
af-group AG_DECIX_ROUTE_SERVERS_6 address-family ipv6 unicast
!! Allow sending of BGP standard communities to control your prefix advertisements
!! For all available communities, please see "Action BGP Communities"
send-community-ebgp
!! Inbound IPv6 policy
route-policy RPL_DECIX_ROUTE_SERVERS_IN_6 in
!! Outbound IPv6 policy
route-policy RPL_DECIX_ROUTE_SERVERS_OUT_6 out
!! Please set maximum-prefix limit IPv6 mentioned in the RS Guide/Peering DB
!! maximum-prefix 75
!! Strip private ASNs from BGP AS-PATH
remove-private-AS
!! Optional: Keep a pre-ingress-route-map copy of the peer table even if route refresh is supported (if you have the memory; useful for debugging)
soft-reconfiguration inbound always
!
session-group SG_DECIX_ROUTE_SERVERS
!! ASN of DE-CIX route servers
remote-as 56858
!! Please do not use aggressive timers (60/180 should be fine) to reduce the risk of flapping sessions
timers 60 180
!! Our route servers are transparent: Ignore first AS in AS path not being your peer AS (i.e. 56858)
enforce-first-as disable
!! Allow BGP graceful restart
graceful-restart
!! The route servers are passive and waiting for you side to initiate the sessions
session-open-mode active-only
!
neighbor-group NG_DECIX_ROUTE_SERVERS_4
use session-group SG_DECIX_ROUTE_SERVERS
address-family ipv4 unicast
use af-group AG_DECIX_ROUTE_SERVERS_4
!
!
neighbor-group NG_DECIX_ROUTE_SERVERS_6
use session-group SG_DECIX_ROUTE_SERVERS
address-family ipv6 unicast
use af-group AG_DECIX_ROUTE_SERVERS_6
!
!
neighbor 185.1.172.252
use neighbor-group NG_DECIX_ROUTE_SERVERS_4
description RS1.SEECIX.NET
!
neighbor 2001:7f8:f5::de1a:a:1
use neighbor-group NG_DECIX_ROUTE_SERVERS_6
description RS1.SEECIX.NET
!
neighbor 185.1.172.253
use neighbor-group NG_DECIX_ROUTE_SERVERS_4
description RS2.SEECIX.NET
!
neighbor 2001:7f8:f5::de1a:a:2
use neighbor-group NG_DECIX_ROUTE_SERVERS_6
description RS2.SEECIX.NET
!
!
end